Open Banking in Hong Kong to Fuel The City’s Fintech Ambitions
by Fintech News Hong Kong October 1, 2018Open banking is gaining traction globally fueled by regulations like the EU’s PSD2 and the UK’s CMA Open Banking, a combination of banks’ internal efforts and market initiatives.
Open banking refers to the use of open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable developers to build applications and services around financial institutions.
APIs are a set of rules that govern how one piece of computer software communicates with another. If adopted, these enable banks’ customers to share their personal financial information with third parties to generate opportunities for better deals on financial products and to compare products more easily.
From the banks’ perspective, the technology enables them to remain competitive by providing them with opportunities to provide improved, customer-friendly services and reach out to untapped markets.
The open banking concept changes how banks deal with customers’ financial information. The whole motivation behind it is to bring more transparency, competition and innovation to financial services, which in turn, would lead to better and fairer access.
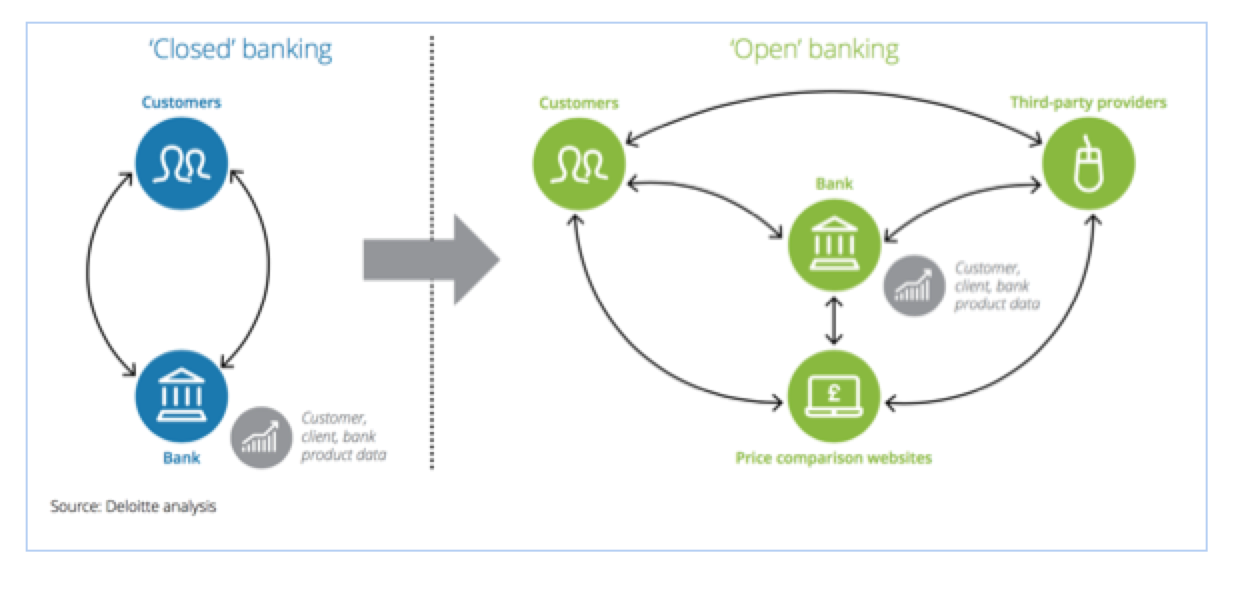
Open Banking Hong Kong — Where Does it Stand?

Image credit: The Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Wikipedia
Propelled by the UK and the EU, open banking is now arriving in Asia with many markets following suit with the regulatory trend.
Hong Kong has also gotten on board, with the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA)’s Open API initiative and the regulator’s commitment to building a healthy banking open API ecosystem to keep up with worldwide development on the delivery of banking services.
The new framework takes a risk-based principle and a four-phase approach to implement various open API functions, and formulates recommendations to ensure fast adoption and security.
It also lays out detailed expectations on how banks should onboard and maintain relationship with third party service providers to ensure consumer protection.
The HKMA believes that the framework will serve as an important guide for the banking industry in Hong Kong to adopt APIs effectively and strike a good balance between innovation and risks.
The regulator expects banks to begin deploying the strategy within six months and said it will work closely with the industry in the next 12 months on the deployment.
On July 23, the day of the launch of Open API, the HKMA published 50 sets of financial data and important information opened via API.
These cover information most frequently accessed by the public such as statistics on the HK dollar exchange rates, interest rates, the banking sector and the Exchange Fund, and press releases and Coin Cart schedule. The remaining 80 sets of information will be opened via API in phases and to completion by mid-2019.
By mandating banks to make their customers’ data accessible to third parties and encouraging the use of open APIs, the regulator is encouraging innovation and championing collaboration between third party fintechs and traditional banks.
Norman Chan, chief executive of the HKMA, has said that open API was “one small step for a bank, but a milestone for financial innovation in the banking sector.”
One bank that’s committed to open banking is Citi. A spokeswoman for Citi in Hong Kong told the South China Morning Post in January that the bank had already launched open APIs and that seven categories were available to Hong Kong developers.
In May, the bank announced its partnership with six corporations in Hong Kong to empower and accelerate the open API development and acceptance. Citi has launched APIs in categories such as Onboarding, Cards, Customers, Pay with Points, and Money Movement.

(From left to right): Mr. Paul Jung, Head of Products, Northeast Asia, Visa; Ms. Kathy Wong, Head of Travel, Zurich Insurance (Hong Kong); Mr. Ricky Wong, Chairman, Hong Kong Television Network Limited; Mr. Howard Lee, Deputy Chief Executive of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority; Ms. Angel Ng, Citi Country Officer, Hong Kong and Macau; Ms. Pauline Teoh, Chief Partnership Distribution Officer, AIA International Limited; Mr. Sunny Cheung, Chief Executive Officer, Octopus Cards Limited; Ms. Patricia Lee, Executive Director, EGL Tours.
In July, it said that it has added three new API partners in Hong Kong. EGL Tours, Watsons and Fortress joined the “Citi API ecosystem” and committed to integrate the Citi Pay with Points API with their e-commerce platforms, enabling Citi cardholders to offset online purchases using their reward points instantly after checkout.
The formulation of the Open API Framework is one of the seven initiatives announced by the HKMA in September 2017 to prepare Hong Kong to move into a new era of Smart Banking. Other initiatives include the promotion of virtual banking, enhanced research and talent development, and the development of a more efficient and faster payment system.
Featured image via Ruslan Bardash on Unsplash