
Hong Kong’s Open API Ambitions Expands to the Insurance Sector
by Fintech News Hong Kong December 14, 2021The Insurance Authority (IA), Hong Kong’s insurance regulator, is exploring the development of an open application programming interface (API) framework and has established a working group focused on the initiative, Tony Chan, the associate director of policy and development at the IA, said in a keynote speech at a recent event.
The plans were shared during the Actuarial Society of Hong Kong (ASHK)’s 19th Appointed Actuaries Symposium on November 23, 2021, during which Chan stressed the need to foster greater collaboration among insurers, third-party service providers and regulators.
Some insurers are already utilizing API technology to facilitate connectivity between their platforms and their business partners, he said, and greater adoption of API technologies is expected moving forward.
Recognizing the importance of open API in the insurance sector, he said the agency is looking to introduce an Open API Framework to further boost collaboration between stakeholders and facilitate data sharing within and beyond the insurance industry.
On this, the IA has established a working group on open API, Chan said, which will serve as a platform to exchange ideas on key issues, scope, pilot use cases and implementation timeline.
API technologies are bringing new business opportunities, including improved customer experience and personalized services, he added, and can also help narrow protection gaps, promote financial inclusion and enhance financial connectivity.
Implementation of Open API Framework progresses in the banking sector
News of the IA’s open API framework comes on the back of the ongoing rollout of the Open API Framework for the banking sector, a major initiative under the broader Smart Banking plan unveiled in 2017.
Implementation of the Open API Framework was kickstarted back in 2019 by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA).
So far, the first two phases have already been implemented and saw over 20 retail banks participating with the launch of more than over 800 open APIs covering a wide range of banking products and services.
An industry survey by Accenture commissioned by the HKMA found that popular Phase I and Phase II retail banking use cases included product and service information enquiries, real time product and service comparison, and streamlined product and service subscription..
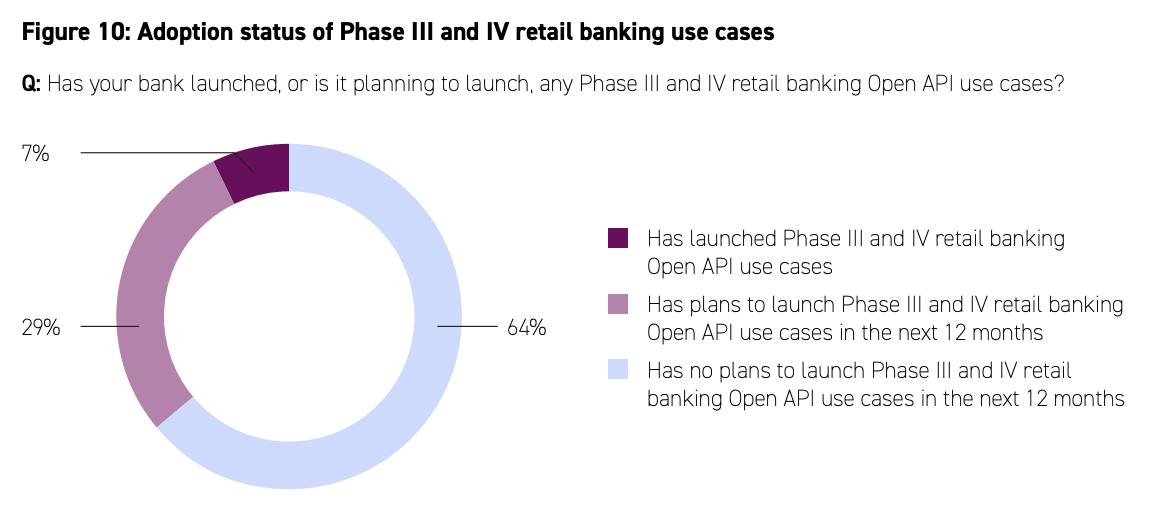
Adoption status of Phase III and IV retail banking use cases, Source: The Next Phase of the Banking Open API Journey, Accenture/HKMA
Phases III and IV will be implemented progressively with the initial batch of API functions covering deposit account information and online merchant payments expected to be implemented by the 28 participating banks starting from December 2021.
Details are still being worked on and two sets of guidance documents are scheduled to be published by the end of the year: a set of standards covering key areas including customer experience and authentication, technical and data standards, information security and operation standards; and a refined version of the Common Baseline document that will include the scope of Open API Phase III and IV implementation.
Several Hong Kong banks have however not waited for the implementation timeline for Phases III and IV and are proactively advancing banking open API development.
Of the 28 banks surveyed by Accenture, 36% have already launched, or are planning to launch, related use cases, including account information aggregation services (50%), transaction initiation services (50%), and personalized products and services (30%).
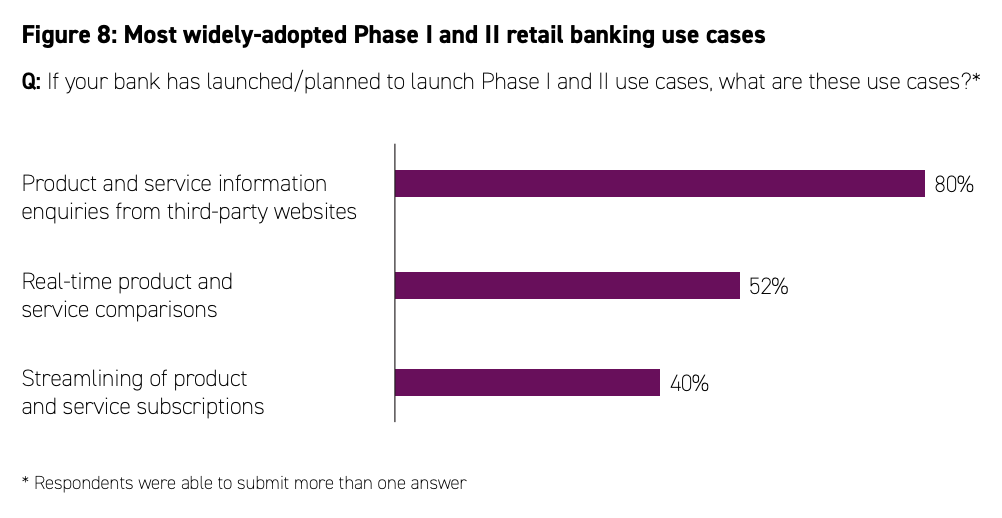
Most widely-adopted Phase I and II retail banking use cases, Source: The Next Phase of the Banking Open API Journey, Accenture/HKMA
Expanding the open API framework beyond retail banking
Although the Open API Framework focuses primarily on retail banking, Hong Kong banks are also extending the framework to other banking businesses, including commercial and small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) banking.
Out of 28 Hong Kong banks polled, 45% have launched, or are planning to launch, commercial and SME banking use cases related to banking open APIs. These use cases include the prefilling of information for loan applications on third-party websites, enquiries on loan interest rates or foreign exchange rates, foreign exchange transfers or account payable settlements from third-party websites, and account information aggregation from different bank accounts.
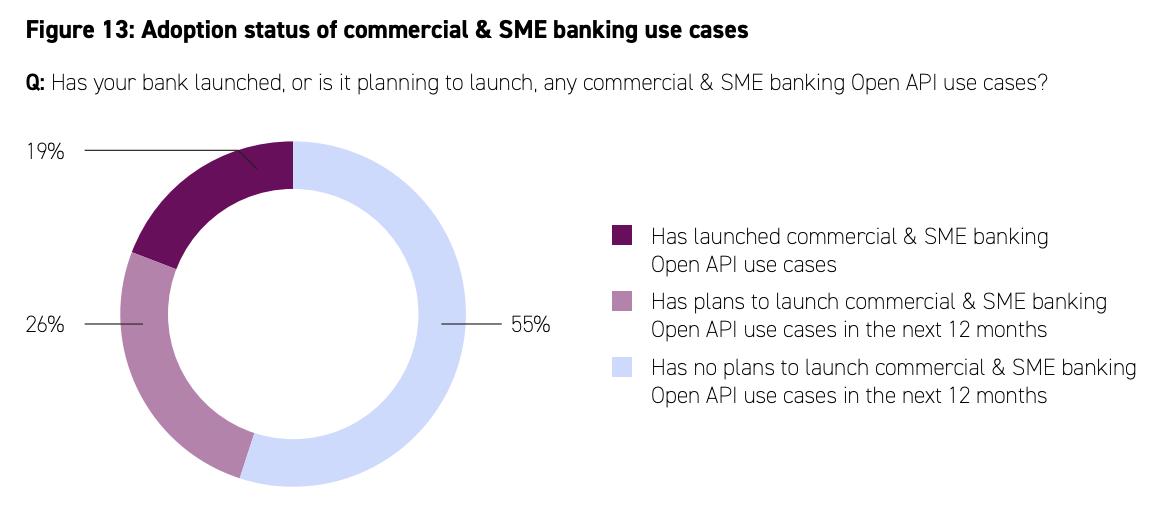
Adoption status of commercial and SME banking use cases, Source: The Next Phase of the Banking Open API Journey, Accenture/HKMA








